By Ismael Peña-López (@ictlogist), 03 June 2008
Main categories: Cyberlaw, governance, rights, e-Government, e-Administration, Politics, Meetings, Participation, Engagement, Use, Activism
Other tags: blog, carles campuzano, idp2008, lourdes muñoz santamaria, roc fages, web 2.0
2 Comments »
Notes from the 4th Internet, Law and Politics Congress.
Session VI
Round Table
Public opinion and participation on the internet: blogs and political parties
Lourdes Muñoz, member of parliament, (PSC). PSC Secretary for Women’s Policy.
Politicians and their participation in the Web 2.0 is but a part of a higher goal which is the development of the Information Society.
The Web 2.0 provides new means for both citizens and institutions to have new channels to have their message sent, and their opinion heard. Indeed, there’s an increasing amount of readers and creators of blogs.
And not only opinion, but participation.
Some facts and figures about the penetration of blogs in the Spanish Congress
There is not a big difference between male and female members or the Parliament having blogs, though there is a regional difference, where Catalonia has a higher average of blogging members than the Spanish State level.
Uses of blogs by politicians
- Inform themselves
- Inform their audiences
- Give arguments about their opinions (e.g. the ones stated off-line in shortest timespans)
- Show their own ideas, especially in huge parties where the institutional voice is shadeless
- Show their agenda, what they do
- Be specific in their opinions, get into the detail of their specialty… and get feedback
- Listen to the ones affected by their decisions, by experts on a specific field
- Include the opinions they get
- Interact with your audience
- Share knowledge, especially the one that the politician has because of their privileged position
- Participate in other spheres and platforms
Blogs enable picking the anonymous citizenry as an aggregate of individuals, so a (more or less) personalized message can be sent.
 Carles Campuzano, Lourdes Muñoz, Roc Fages
Carles Campuzano, Lourdes Muñoz, Roc Fages
The thrilling thing about blogs is that they enable a debate without boundaries: geographical, created among and within political parties, ideological, of different levels of commitment, etc.
Blogs help the free flow of ideas, breaking endogamous structures and hierarchies. Individual voices are boosted to higher levels of relevance. And this free flow of ideas applies for those having similar ideas so they can exchange them, but also for those having opposed ideas so a debate takes place.
The problem with the so far adoption of the Internet by political parties is that the message hasn’t changed: they’re used the same way the institutions have used the media to send their message out. The blogger politician should be not the exception, but the trojan horse to change the system from within.
And a caveat and a proposal: blogs enable the organized citizenry to send their message out too, but their representativeness can also be not as real as one might think. But the politician can both listen to organized lobbies and also to the individuals they supposedly represent.
The immediate response to the citizens is not only about transparency and accountability, but also to get richest feedback and act according to it.
Roc Fages, specialist in communication on the Internet.
We have to go beyond the tools of the Web 2.0, but to adopt the concept: listen, interact, create networks, etc. between people, and especially enabling the citizenry to create their own networks.
There are plenty of political blogs, but few politicians’ blogs. There’s an increasing trend where not only established politicians blog, but also the partisans of the political parties, which is a rich arena where interesting ideas are created.
Citizens are already moving on to engage in campaigns. Some politicians do have blogs. Can institutions (e.g. the Parliament) engage in the conversation and collaborate with Web 2.0 applications? Fix My Street is an interesting example.
Are politicians a brand that has to be curated on the Internet?
Another point to be made is that the Web 2.0 is a perfect bridge to reach the Nintendo Generation and hence reduce (or try to) political disaffection (they’re the voters of the future).
Key points
- Without attitude 2.0, there’ll be no politicians 2.0
- Individual effort will bring benefits when it brings collective benefits.
- Offline + online.
- Actions to dynamize the Net.
- No fear to engage in public-private partnerships.
- The potential of the Nintendo generation
Q&A
Marc López: What’s the role of the corporate sector? Do they monopolize the political debate leaving the citizen (individual) participation without room? CC: The big issues are discussed not on governments, but on the public arena and within the public-private debate. Web 2.0 makes it more open and transparent. RF: the problem is that firms are more flexible, but the Web 2.0 should help in bringing flexibility to the institutions.
Ignacio Beltrán de Heredia: how do we cope with the tight control parties have on the message that is sent about them and this supposed freedom of speech by their own members? LM: Parties send their “canned” message, but they’re open to e.g. the participation of bloggers in their events. So it’s true that the citizenry is having their voice heard. CC: Parties are trying to keep the control, but it’s useless. It actually is becoming the other way round: media (corporate and citizenship) are taking the control of the parties’ inner agendas. RF: A main driver for leakage of non-official information for political parties is not outsiders, but insider partisans that are not part of the powers of the party.
Some attendee: what’s the reason of the difference between political parties in Spain and the US concerning the adoption and use of Web 2.0 tools? LM: The US is doing great… for the people that already is online, but is seemingly to be forgetting about the others. RF: The pervasiveness in the US of the political discourse is absolute, and this helps to engage people to vote or to volunteer for campaigning. What is true is that spaniards use the Internet for e-commerce issues, but not for political ones. There’s an evident gap here: is it about e-readiness or about politics?
Another attendee: if the web can be used all days of the year, including pre and post-campaing seasons, or be written and read from wherever, shouldn’t we be changing some electoral regulations? Open lists, propaganda regulation, etc. LM: Of course some laws are outdated. CC: politicians are to tied to their stakeholders (the powers of the party, lobbies, etc.) and this is corrupting the essence itself of democratic representativeness. This should be changed and, maybe, the Web 2.0 can help in doing it.
Francesc Muñoz: How many citizens can engage in Politics 2.0? And not because of access, but culture, social class. Isn’t it a utopia? RF: An example: in the Netherlands, the Maghribian community gathers around telecenters and virtual communities. These virtual communities are riches in opinion about their daily lives and they do present a great opportunity for the politicians to approach that community. And the good thing about this is that people no more needs to seek for information, because it is information that does seek and reach its audience. CC: Maybe there’s not many people actually using these technologies, but they are the first wave of an upcoming, nearest, changing, future.
4th Internet, Law and Politics Congress (2008)
By Ismael Peña-López (@ictlogist), 10 May 2008
Main categories: e-Government, e-Administration, Politics, Meetings, Participation, Engagement, Use, Activism
Other tags: blog, fernando tricas, icities, javier estevez, jose luis prieto, pau llop, victor ruiz
No Comments »
iCities is a Conference about Blogs, e-Government and Digital Participation.
Here come my notes for session VII.
Round Table: Networked Citizens. Blogs, Where to?
Chairs: Pau Llop
Blogs come from the participative sites that flourished after the Slashdot experience, both technically and conceptually.
Blogs have been an evolution of forums, but only at the usability level, but the general idea has not really changed that much.
And like forums, they are of short reach. Only 6% of the population read political blogs… but we keep telling politicians that they have to be on the Net and have their own blog. Does this make any sense at all? When everyone has a blog (if that ever happens), will we at last make of them an influential tool?
Some questions about the state of blogging
- Whose are my data?
- Who’s the master?
- What’s true?
- Near? Far?
- How do I see it? Where from?
- Who are you? Who am I?
Forecast
- Normalization of the blog phenomenon
- Tools will be improved: they are not that easy to use…
A challenge: threats to sites/blogs related with intellectual property rights, privacy, etc.
There is an increasing trend in Internet users reducing their amount of time watching TV. Besides other browsing, they can now reach TV content on the Internet, especially videos.
Investment in Internet grows at a 50% rate, while in general broadcasting media grows below the inflation rate (which means that actually decreases). As an example, investment in blogs duplicated last year, investment in videos was multiplied by four, etc.
Citizen journalism:
Blogs are the only way to avoid the (total) commercialization/commoditization of the Internet.
Personal blogs (i.e. blogs about personal stuff) are majority. Politicized, reflection, journalist-like blogs are minority. Influence of the latter?
They might not be influent individually, but in aggregate terms, they at least generate some buzz and can raise awareness and generate some reactions… not on the citizenry at large, but on firms and lobbies that see their brands or interests menaced.
The upsetting answer to this has been legal threats that sometimes end well and sometimes don’t.
iCities 2008, Blogs, e-Government and Digital Participation (2008)
By Ismael Peña-López (@ictlogist), 09 May 2008
Main categories: Digital Literacy, e-Government, e-Administration, Politics, e-Readiness, Meetings, Participation, Engagement, Use, Activism
Other tags: Activism, blog, e-Government, education, Engagement, icities, jaume morego, julio meneses, Participation, Engagement, Use, Activism, ricard ruiz de querol, Use
4 Comments »
iCities is a Conference about Blogs, e-Government and Digital Participation.
Here come my notes for session I (part I).
Digital Citizens vs. Analogue Institutions
Ismael Peña-López
These are the materials I’m using at the iCities: Primeras Jornadas sobre Blogs, e-Government y Participación Digital [First Conference on Blogs, e-Government and Digital Participation], for the opening speech, in which I take part on Friday 9th May 2008.
Slides:
Universal McCann (2008).
Wave 3. New York: Universal McCann.
Acknowledgements
Update:Now that the conference is over, hearty and warmest thanks to
Pablo Díaz and
César Calderón for making the conference happen and for having invited me.
Ricard Ruiz de Querol deserves my sincerest gratitude for his always challenging insights about the Information Society. Jaume Moregó also pushed me to a project that payed back with good reflections. A good buch of this conference was inspired by them both, thank you. And also thanks to Julio Meneses for his lightning fast and valuable help with some graphic materials.
iCities 2008, Blogs, e-Government and Digital Participation (2008)
By Ismael Peña-López (@ictlogist), 07 May 2008
Main categories: e-Government, e-Administration, Politics, ICT4D, Meetings, Participation, Engagement, Use, Activism
Other tags: blog, helen milner, icities, web 2.0
No Comments »
There is a constant buzz on the importance of blogs as both proxies for the freedom of speech in one country and also as the paradigmatic tool for citizen participation, activism, advocacy and so on. But, what’s the reality behind this (strong) statement? Is it just the mad dream of an enlightened digerati, or is there some truth in blogs politically empowering the citizenry?
These are some of the questions behind iCities: Primeras Jornadas sobre Blogs, e-Government y Participación Digital [First Conference on Blogs, e-Government and Digital Participation]. Preparing the opening speech, which I impart on Friday 9th May 2008, I found some interesting things.
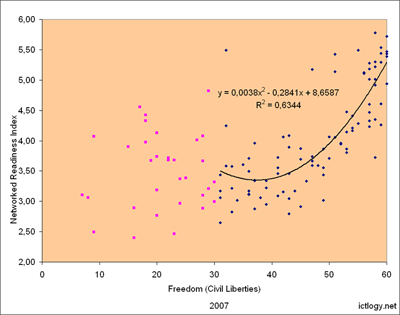
Even if data have to be taken with maximum care and minimum work was performed on the statistical apparatus, it does seem that there is a relationship between the amount of existing liberties in one country and its degree of development of the Information Society. Data come from the Freedom Aggregate Scores published at the Freedom in the World 2007, and the Networked Readiness Index published at the Global Information Technology Report 2007-2008: Fostering Innovation through Networked Readiness.
First chart compares the Networked Readiness Index (Y) with the Civil Liberties score (X). We can see that, beyond a threshold (here arbitrary set at the 50% of the total score), there is a relationship where the more rights, the more developed an Information Society is. Or the contrary: as no causality has been analyzed, we can also state that the more digitally advanced a society is, the freer. Anyhow, these are two variables that do go hand in hand.
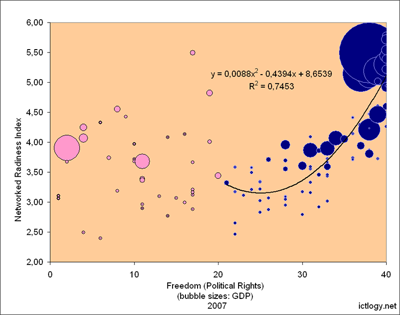
But the next chart is even more interesting. This second chart compares the Networked Readiness Index (Y) with the Political Rights score (X) — again split in two at the 50% of the total score (democratic vs. not democratic). First thing we can see is that the relationship tightens: political freedom seems to be really important for e-readiness, for the development of the Information Society. Surprising? Not really: once the main infrastructures are set, e-Readiness strongly depends, for it to increase, on market liberalization, e-Government, content, communication channels, users… If you want these variables to increase, it looks plausible that freedom and participation is a must.
But we have added, as the buble size, the Gross Domestic Product (the bigger the bubble, the bigger the country’s GDP). This gives us, at least, two more hints:
- First one: beyond a threshold, you’re e-readiness won’t grow despite the power of your economy. The two big pink bubbles on the left are China (far left) and Russia. Their GDP is quite big (let’s not forget that there are only +120 countries plotted in this chart: most of the remaining +100 countries/territories just “don’t count” as per e-readiness matters because they are too poor to). But both Russia and China seem to have topped a crystal ceiling on e-Readiness development. Could it be because of the evident lack of liberties in these countries?
- Second one: in the Information Society, the international environment matters. Malaysia and Singapore are the two pink dots on the upper part of the chart, almost in the horizontal middle. The first thing to say is that, even if they are but democratic, they are nor the typical corrupted and/or tyrannic system. On the other hand, they are surrounded by ICT early adopters, which is something Helen V. Milner has already pointed as being very important to set an Information Society agenda in her work The Global Spread of the Internet: The Role of International Diffusion Pressures in Technology Adoption. Nevertheless, these are two interesting exceptions that surely need deeper analysis.
Summing up
- Are blogs a good measure of (a) the freedom in a country and (b) the degree of development of a country’s Information Society?. Maybe. What seems clear — though more and better analysis should be performed — is that these are social variables that go together.
- Are non-democratic regimes to survive the Information Society? Who knows. But, again, it seems clear that there is a trade off between authoritarianism and digital development. The rulers — and their citizenry — will perhaps have to choose between democracy and digital development or keeping the power. But power cannot be kept at all costs and against all odds. How much will the e-excluded tolerate losing the digital train towards development?
By Ismael Peña-López (@ictlogist), 07 April 2008
Main categories: Education & e-Learning, Meetings, Participation, Engagement, Use, Activism
Other tags: blog, education 2.0, instructional technology, km, pim, pkm, web 2.0, wiki
2 Comments »
The Canadian Institute of Distance Education Research, University of Athabasca, has invited me to impart a seminar in the framework of the CIDER Sessions about my digressions around The Personal Research Portal. The focus here will be on the educator, as I did in my article El portal personal del profesor: El claustro virtual o la red tras las aulas [The Personal Research Portal: The Virtual Faculty or the Net behind the Classroom].
The seminar will take place online — using Elluminate — on Friday 11th April 2008, at 17:00h GMT (in English).
Relevant info
Abstract
Instructional technology has suffered, in our opinion, two revolutions and a half during the last decades. The first one was, there is no doubt, the introduction of the personal computer in the educational environment. The second one, the appearance of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) in a broader sense – that implied, among other things, connecting the PC to the network – and their use in teaching. The “half” left, as it actually is a corollary of the latter, the one brought by the so called Web 2.0, thus giving birth to what has been dubbed as Education 2.0.
Notwithstanding, the emphasis has been put, most of the times, in how these technologies impact the relationship between teacher and student or how these technologies whether and how enhance the learning process and its results: how can ICTs be used to improve education administration, how can they help teaching in a classroom, applications in distance learning, etc.
Our aim in this seminar is to shift out of the spotlight and focus on the “hidden” practices of education, to stress on all the tasks that happen outside the classroom – be it of bricks and mortar or virtual – before or when designing a subject or teaching it to the students, what happens after that teaching, etc. in this necessary phase of reflection and redefinition of concepts, syllabuses, practices and so on… but without students. We want to make some proposals on how educators can use ICTs in their more open, participative and social side to build themselves a place on the net, to weave their own network of colleagues, to share resources, exchange experiences or suggest doubts and questions to the rest of education professionals.
Our ultimate goal would be to highlight that we think it is possible to build a virtual faculty based on their personal portals built with Web 2.0 tools, way beyond teacher spaces inside virtual learning environments or other corporate tools from educational institutions, thus leaving room for individual initiative and, most important, digital presence and digital identity.
Acknowledgements
Sincerest thanks go to Lynn Anderson for the proposal, all the e-mailing that we’ve been having through the last weeks and the support in preparing the seminar.


 , 15 Mb)
, 15 Mb)